Media's Political Influence | Analyzing Narratives
Explore how the media impacts politics and public opinion. Analyze the role of media narratives in shaping political views .

The Power of the Media: Shaping Political Narratives and Public Opinion
The media, in all its diverse forms, plays an indispensable role in shaping political narratives and molding public opinion. In today's digital age, where information flows freely and swiftly, the media's influence on politics and society has reached unprecedented heights. This article delves into the multifaceted role of the media in influencing political narratives and public opinion, exploring how it can both enlighten and manipulate, educate and misinform.
The Media as the Fourth Estate
The media has long been referred to as the "Fourth Estate" of government, symbolizing its pivotal role in maintaining a functioning democracy. Its primary responsibility is to act as a watchdog, holding those in power accountable and ensuring transparency in government actions. Through investigative journalism, the media exposes corruption, abuse of power, and other wrongdoings, which can significantly influence public opinion.
Agenda-Setting and Framing
One of the most critical ways the media shapes political narratives is through agenda-setting and framing. Agenda-setting theory posits that the media can influence the importance attributed to specific issues by highlighting them through extensive coverage. When the media devotes substantial attention to certain topics, the public perceives them as more significant.
Framing, on the other hand, involves presenting issues or events in a particular light. By framing a story in a specific way, the media can influence how the public interprets and reacts to it. For example, framing an economic downturn as a result of government mismanagement may lead the public to demand political change.
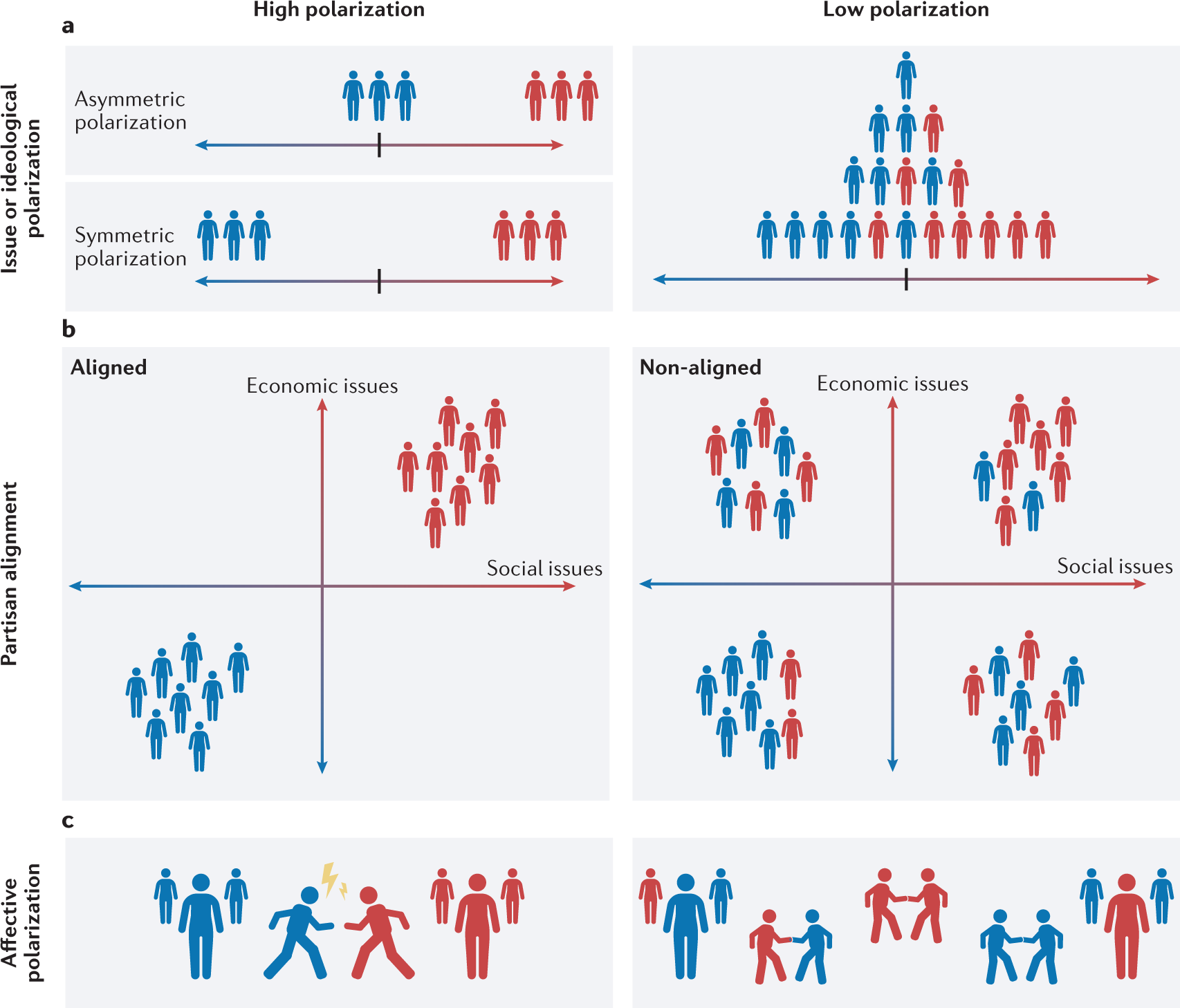
Political Bias and Polarization
Media outlets, both traditional and digital, often have political biases that can significantly affect their reporting. This bias can contribute to political polarization, where individuals are exposed to information that reinforces their existing beliefs, leading to more extreme views and a divided society.
The rise of partisan news outlets and social media echo chambers has amplified this effect, as people tend to consume news that aligns with their political ideology. This further deepens divisions and makes it increasingly challenging to find common ground in political discourse.
Public Opinion and Social Media
The advent of social media has transformed the media landscape, giving individuals the power to share their opinions and engage in political discussions on a global scale. Social media platforms can be both a force for positive change and a source of misinformation. They enable grassroots movements to organize and gain momentum, as seen in the Arab Spring and Black Lives Matter protests.
However, social media also facilitates the rapid spread of false information and echo chambers, where individuals only interact with like-minded people, reinforcing their existing beliefs. This can lead to the creation of alternative realities and the erosion of trust in traditional media.
The Role of Fact-Checking
In response to the spread of misinformation, fact-checking has emerged as a crucial component of the media's responsibility. Fact-checkers scrutinize political claims, statements, and news stories, helping the public distinguish between truth and falsehoods. Fact-checking organizations play a vital role in holding politicians and media outlets accountable for their statements.
Media Ownership and Concentration
Media ownership and concentration also influence the shaping of political narratives and public opinion. When a small number of conglomerates own a vast majority of media outlets, it can limit the diversity of voices and perspectives in the media landscape. This concentration of ownership can lead to a homogenized narrative that serves the interests of the owners or advertisers.
The Role of Investigative Journalism
Investigative journalism serves as a powerful tool in uncovering hidden truths and holding those in power accountable. Investigative journalists often risk their safety and reputations to expose corruption and injustice. Examples include the Watergate scandal and the Panama Papers leak, which had far-reaching political consequences.
Media Literacy and Critical Thinking
In an era where misinformation can spread rapidly, media literacy and critical thinking skills are more crucial than ever. The media can shape political narratives and public opinion, but individuals must also be discerning consumers of information. Teaching media literacy in schools and promoting critical thinking can help citizens navigate the complex media landscape effectively.
The Role of Public Relations and Spin
The media landscape is not solely shaped by journalists and news outlets. Political actors, corporations, and interest groups employ public relations and spin tactics to influence narratives and public opinion. Through carefully crafted press releases, staged events, and strategic messaging, they attempt to shape how their actions and policies are portrayed in the media.
Public relations efforts often aim to divert attention from negative stories, control the narrative, or even create distractions to minimize damage. The media's susceptibility to these tactics underscores the importance of investigative journalism and critical analysis to uncover hidden agendas and present a balanced view of events.
Globalization and International Media
In an interconnected world, the influence of media extends beyond national borders. International media outlets and global news networks play a significant role in shaping public opinion about international affairs and geopolitics. How these media organizations frame global events can influence public sentiment, foreign policy decisions, and even international diplomacy.
Moreover, the internet has made it easier for individuals to access foreign news sources and engage in cross-border discussions. This globalization of media enables citizens to develop a more comprehensive understanding of global issues, but it also raises questions about the authenticity and reliability of information from different sources.
The Impact of Technology and Algorithms
Advancements in technology, particularly algorithms and artificial intelligence, have transformed the way media operates. Online platforms, such as search engines and social media, use algorithms to curate content based on user preferences and behavior. This personalized content delivery can contribute to the formation of filter bubbles, where individuals are exposed only to information that aligns with their existing beliefs.
Moreover, the spread of deepfake technology poses a new challenge for media integrity. Deepfakes can convincingly alter videos and audio recordings, making it increasingly difficult to discern real from fake. This underscores the importance of fact-checking and media literacy in the digital age.
The Responsibility of Journalists
Journalists play a critical role in shaping political narratives and public opinion. Their ethical obligations include reporting facts accurately, providing context, and presenting a balanced view of events. However, journalists also face challenges, such as editorial pressure, corporate ownership, and the need for ratings or clicks, which can sometimes compromise journalistic integrity.
To maintain trust and credibility, journalists must adhere to professional standards and ethical guidelines. Investigative journalism, in-depth reporting, and fact-checking are vital tools for ensuring that the media fulfills its role as a watchdog and educator of the public.
The Media's Role in Elections
The media plays a pivotal role during election cycles, shaping voter perceptions of candidates and issues. Political campaigns rely on media coverage to convey their messages to the electorate. How the media frames candidates and their policies can influence voter preferences and election outcomes.
Media outlets often host debates and interviews with candidates, offering a platform for citizens to assess their qualifications and positions. However, the media's role in elections is not without controversy, as bias and sensationalism can sway public opinion and impact electoral results.
The Evolving Media Landscape
The media landscape is continuously evolving, with new platforms and technologies emerging regularly. Citizen journalism, podcasts, blogs, and online forums have expanded the diversity of voices in the media sphere. While this diversification can promote democratic discourse, it also raises questions about the credibility and accountability of non-traditional media sources.
Additionally, the business models of traditional media outlets are under pressure due to declining advertising revenues and the proliferation of free online content. This economic strain can impact the quality and independence of journalism.
The media's role in shaping political narratives and public opinion is dynamic and complex. It wields immense power in influencing how individuals perceive the world, make decisions, and engage in civic life. While the media has the potential to serve as a beacon of truth, it can also be a source of misinformation and manipulation.
In this rapidly changing media landscape, the responsibility falls not only on media organizations but also on individuals to be discerning consumers of information. Media literacy, critical thinking, and a commitment to seeking diverse perspectives are essential for navigating the ever-evolving media landscape and ensuring that the media continues to fulfill its vital role in democracy. As society grapples with these challenges, a well-informed and media-literate citizenry remains the cornerstone of a healthy and vibrant democracy
What's Your Reaction?